Heat pumps are widely used across residential, commercial, and industrial applications because of their efficiency and low carbon impact. In cold and humid climates, however, one operating feature often raises questions among users and technicians alike: the Heat Pump Defrost cycle.
Understanding how the defrost cycle works, when it activates, and how to troubleshoot common issues is essential for maintaining system efficiency and long-term reliability. This article provides a clear, practical overview, with insights relevant to today’s advanced heat pump products.
more article visit: harga ac 1/2 pk – acjakarta.com
What Is a Heat Pump Defrost Cycle?
During heating operation, a heat pump extracts heat from outdoor air. When outdoor temperatures are low and humidity is present, moisture can freeze on the outdoor coil. Frost buildup reduces airflow and heat transfer, causing efficiency to drop.
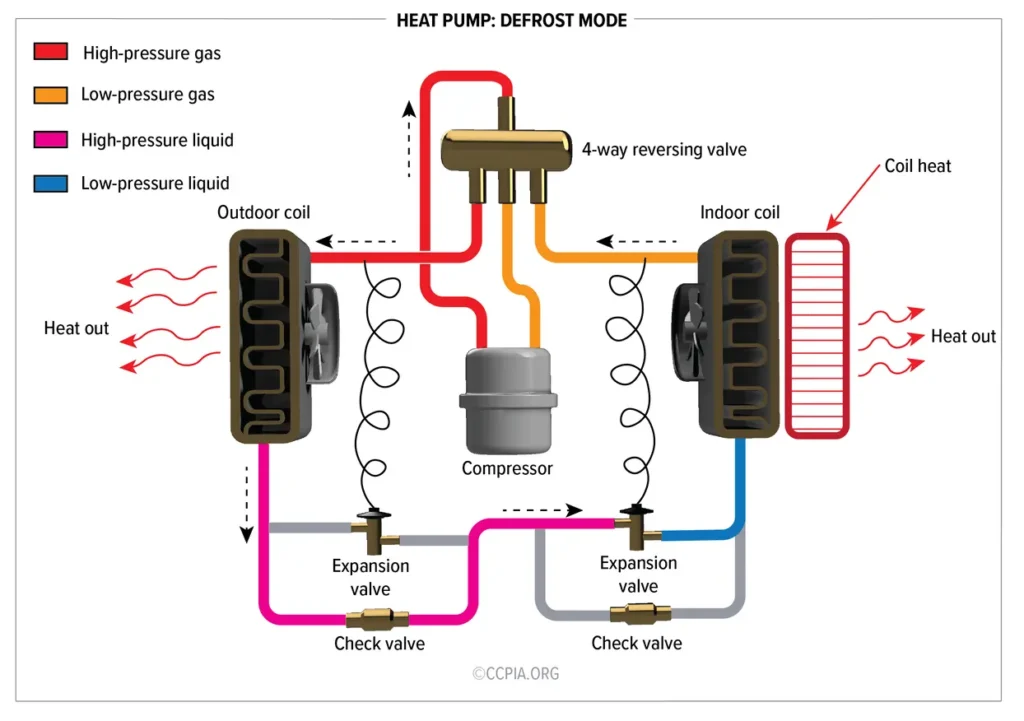
The Heat Pump Defrost cycle is a controlled process that temporarily removes this frost. Instead of relying on external heaters, modern heat pump systems reverse their refrigeration cycle to warm the outdoor coil. This melts accumulated ice and restores normal operation.
Defrost is not a fault or emergency condition. It is a normal, necessary function designed into the system.
How the Defrost Cycle Works
In most air-source heat pumps, defrost is achieved by briefly switching the unit into cooling mode while continuing to heat the indoor space with auxiliary support if needed.
The process typically follows these steps:
- Sensors or control algorithms detect frost conditions on the outdoor coil.
- The system temporarily reverses the refrigerant flow.
- Hot refrigerant passes through the outdoor coil, melting ice.
- The defrost cycle ends once the coil reaches a target temperature or time limit.
- The heat pump returns to normal heating mode.
Advanced heat pump products use intelligent control boards, coil temperature sensors, and adaptive logic to ensure defrost occurs only when needed. This minimizes energy loss and avoids unnecessary interruptions.
When and How Often Does Defrost Occur?
Defrost timing depends on several factors, including:
- Outdoor temperature
- Humidity levels
- System load
- Coil design and airflow
- Control strategy
Older heat pumps often used fixed-time defrost intervals, such as every 30, 60, or 90 minutes. While simple, this approach could trigger defrost even when no frost was present.
Modern systems rely on demand-based defrost, which activates only when sensors detect actual frost conditions. As a result, defrost cycles are shorter, less frequent, and more energy efficient.
In typical winter conditions, a well-designed heat pump may defrost every 60 to 120 minutes, with each cycle lasting 5 to 10 minutes.
What Users May Notice During Defrost
During a defrost cycle, some visible or audible changes are normal:
Outdoor fan may stop temporarily
Steam or vapor may rise from the outdoor unit
Indoor air temperature may feel slightly cooler
System may make a brief whooshing sound
High-quality heat pump products are designed to minimize indoor comfort disruption. Features such as variable-speed compressors and intelligent auxiliary heating help maintain stable indoor temperatures throughout defrost.
Common Heat Pump Defrost Problems
While defrost is a standard function, issues can arise if components fail or settings are incorrect. Common problems include:
Frequent or Excessive Defrosting
This may indicate faulty sensors, restricted airflow, or poor coil drainage. It can also result from outdated control logic.
Incomplete Defrosting
If ice remains after a defrost cycle, the reversing valve, compressor performance, or refrigerant charge should be inspected.
No Defrost at All
A system that never defrosts may suffer from failed sensors or control board issues, leading to severe ice buildup and potential damage.
Long Defrost Cycles
Extended defrost duration often points to low refrigerant levels or reduced system capacity.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips
To keep the Heat Pump Defrost function working correctly, consider the following best practices:
- Keep the outdoor unit clear of snow, leaves, and debris
- Ensure proper airflow around the coil
- Schedule regular professional maintenance
- Verify sensor placement and wiring during service
- Use manufacturer-recommended settings and firmware updates
Modern heat pump products are designed for reliability, but routine inspection remains critical, especially in colder regions.
Why Defrost Design Matters in Heat Pump Products
Defrost performance is a key differentiator in today’s heat pump market. Efficient defrost logic improves:
- Seasonal energy efficiency
- Compressor lifespan
- Indoor comfort consistency
- Overall system reliability
Manufacturers increasingly focus on smarter defrost strategies, combining sensor feedback, inverter technology, and adaptive controls. For building owners and system designers, selecting heat pump products with proven defrost performance is just as important as rated capacity or efficiency numbers.
Final Thoughts
The Heat Pump Defrost cycle is a vital function that enables reliable heating performance in cold and humid conditions. When properly designed and maintained, it operates quietly in the background, protecting the system while preserving comfort and efficiency.
For professionals and end users alike, understanding how defrost works, what to expect, and how to identify potential issues leads to better system operation and longer equipment life. As heat pump technology continues to evolve, intelligent defrost control will remain a core element of high-performance heating solutions.