
The balance sheet (also known as the statement of financial position) reports a corporation’s assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity as of the final moment of an accounting period. For example, a balance sheet dated December 31 summarizes the balances in the appropriate general ledger accounts after all transactions up to midnight of December 31 have been accounted for. Analysts have financial ratios at their disposal to assess this, such as the debt-to-equity ratio (total liabilities divided by the shareholders’ equity).
- A common face value of bonds is $1,000, although bonds of other denominations exist.
- Long-term liabilities are financial obligations that a company will pay back over a period of time greater than one year.
- The corporation issuing bonds may be required to restrict its retained earnings.
- Generally, you can tell a company’s long term and short term viability by comparing it’s long term and short term assets with its long term and short term liabilities.
- A company with a high level of long-term liabilities may be more risky than a company with a lower level of long-term liabilities.
What Happens To Your Student Loans When You Die
- Fees earned from providing services and the amounts of merchandise sold.
- The use of long-term debt affects various stakeholders differently, from investors to company management, and even the broader economy.
- A 15-year mortgage is a long-term liability, but payments due this year are current liabilities.
- Long-term liabilities are a type of long-term debt a company holds on its balance sheet.
- This account includes the amortized amount of any bonds the company has issued.
Your bookkeeper should separate these items to show a more accurate picture of your business’s current liquidity. You can also see from this what your ability is to pay the current liabilities on time. This is because you will not be looking at huge debt upfront but only what’s coming up due. Liabilities represent financial obligations of an entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events.

🧾financial accounting i review
This helps the business grow without needing to buy a building outright. Long-term debt is one of the most common examples of long-term liabilities. It allows businesses to make significant investments without using up all their cash at once. By understanding how it works, you can get a clearer picture of how companies manage their finances. When thinking about “examples of long-term liabilities,” long-term debt is always at the top of the list. Long-term liabilities are an integral part of accounting and understanding their implications https://www.bookstime.com/ is crucial for assessing a company’s financial health and making informed decisions.
Accounting best practices on long term liabilities
Creditors use it to make decisions regarding the extension of credit facilities, which will be used for the growth and expansion of the business. In the balance sheet, they are listed separately, and they are considered to be long-term debts of the company. This is the value of funds that shareholders have invested in the company.

This information is most helpful in trend, so looking at it in comparison to one or two previous fiscal years will help provide more Accounting Errors context for your analysis of the data. Liabilities are a natural “credit balance” meaning that, in an accounting entry, a credit to a liability account will increase it. A negative number (debit balance) in the liabilities section of the SOFP is not normal and should be questioned and explained. Any amount remaining (or exceeding) is added to (deducted from) retained earnings.

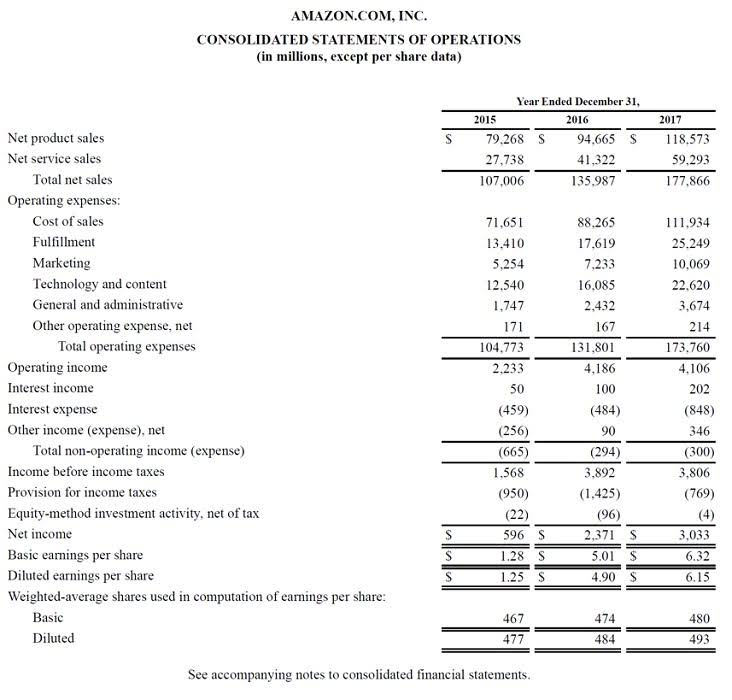
Scrutinizing these intricate details can provide grounded insights into the company’s long-term viability and risk management capabilities. Investors and creditors often use liquidity ratios to analyze how leveraged a company is. Ratios like current ratio, working capital, and acid test ratio compare debt levels to asset or earnings numbers. The company records this as a long-term liability because it doesn’t have to repay the loan immediately. Each year, as the company repays part of the loan, the balance reduces, and the amount due within the next year may be classified as a “current liability.”
- Lease liabilities are a key part of the financial picture for many companies.
- This makes intuitive sense given that the bonds have only been held for two months making interest for two months the correct amount.
- This is because you will not be looking at huge debt upfront but only what’s coming up due.
- When we think about long-term liabilities, long-term debt is often the first thing that comes to mind.
- Companies estimate how much these benefits will cost in the future and record them as long-term liabilities.
- This line item includes all of the company’s intangible fixed assets, which may or may not be identifiable.

Understanding long-term liabilities is important for businesses and individuals alike. Remember, it’s always advisable to consult a financial professional or accountant for personalized advice regarding your specific financial situation. When it comes to long-term liabilities, Amortization and Depreciation are two concepts that have a significant impact on the financial statements of a company. These two methods are used to allocate the cost of long-term assets and liabilities over their useful life and determine the amount of expense that should be recognized in each period. While the two concepts might seem similar, what are long term liabilities they are used to allocate the cost of different types of assets and liabilities.
Typically, the balance sheet date is the final day of the accounting period. If a company issues monthly financial statements, the date will be the final day of each month. The balance sheet is one in a set of five financial statements distributed by a U.S. corporation. To get a complete understanding of the corporation’s financial position, one must study all five of the financial statements including the notes to the financial statements. Any liability that’s not near-term falls under non-current liabilities that are expected to be paid in 12 months or more.
